Beta-agonists
Beta-agonists are bronchodilator medicines that open airways by relaxing the muscles around the airways that tighten during an asthma attack.
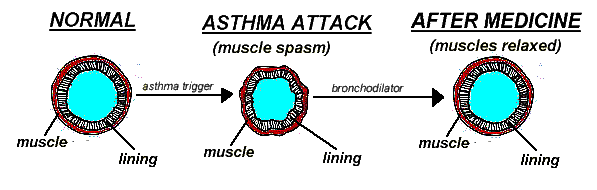
Beta-agonists come in many different forms. Some common beta-agonist medicines are:
- albuterol
- Alupent
- Brethine
- metaproteronol
- Metaprel
- Proventil
- Salbutamol
- terbutaline
- Ventolin
There are also many ways to take beta-agonist medications. They can be:
- inhaled using a metered dose inhaler,
- inhaled using a nebulizer
- inhaled using a dry powder inhaler,
- swallowed as a liquid or tablet, or
- taken as shots.
Inhaled beta-agonists are good at stopping mild asthma attacks and are good a preventing asthma attacks that are caused by exercise. Some people use these medicines every day (three to four times a day) to keep their asthma under control.
Side Effects of Beta-Agonist Medicines
Sometimes asthma medicines make people feel weird or sick at the same time the medicine is making their asthma better. These weird or sick feeling are called side effects. Some of the side effects that people can get from beta-agonists are
- your heart beating very fast
- feeling very shaky or nervous
- feeling scared or worried
- feeling sick to your stomach (nauseous)
Most of the time, these side effects get better as your body gets used to the medicine.
Sometimes, side effects are so bad that people can't take the medicine any more. Some of these type of side effects are:
- bad pain in the chest
- your heart beating very fast or irregularly
- feeling very dizzy
- feeling very sick to your stomach (nausea) or vomiting
Call your doctor right away if you, or anybody you know, has any of these side effects.
Beta-agonist medicines may help people with asthma but they don't make swelling in the airways go away. They also don't prevent swelling in the airways. When people need to use beta-agonist medicines a lot, it may mean that the swelling in the airways is getting worse. If you need to use a beta-agonist medicine every day or if you use it more than three or four times in a single day, your asthma may be getting much worse. You may need another kind of medicine, and you need to talk with your doctor right away.
Send comments to Witz@Virginia.edu
All contents copyright (C) 1996, Stephen M. Borowitz. All rights reserved
Revised: October 20, 1999.